There is a tonne of misconceptions about cloud and fog computing because it is a rather new concept. The term fog computing was coined by cisco in 2014 and only a few people still know about it. People that hear the terms cloud and fog computing think that they are two separate architectures. However, that is not the case at all.
To put it in the simplest words, the fog layer is an additional layer between the cloud itself and the user end devices. But there is more to it so let us get the fog and cloud computing basics down first and we will get into more detail about cloud vs fog computing after that.
What is Cloud Technology?

Cloud computing is a pretty common concept today because it has been here for a long time. Moreover, it has been implemented widely by huge organizations and corporate businesses. More and more businesses are shifting towards cloud computing and cloud-based web hosting because of its advantages over traditional hosting technologies.
Most people know the cloud computing basics so here is a very brief introduction to cloud computing. Cloud is a network of devices connected to each other over the internet. In simple words, it consists of two main layers. The front-end layer consists of the user-end devices such as computers, mobile devices, etc. The second layer is the back-end layer which consists of remote servers located across the globe.
These two layers communicate with each other directly via wireless connections to provide the users with three types of services. These services are IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) means that a user will have access to a server which gives him storage capacity, networking, and processing power. Platform as a Service (PaaS) means that a user is given a development tool with excellent features to create and launch his own applications. SaaS is a pre-made software provided to different types of businesses to aid with their work.
Advantages of Cloud:
Now that you have an idea of what is cloud technology. Let us talk about some of its advantages.

Great Uptime:
We know that cloud is not based on a single physical server. Instead, it is a network of different data centers that are connected to each other and located in different areas of the world. Even if one of the servers has technical issues, the other server can make up for it. Of course, there will be some increased latency but it is better than having no access at all.
Highly Scalable:
Cloud is highly scalable. You can get access to virtually an unlimited amount of storage and computing capacity. You can simply keep on adding more and more resources to your package according to your needs. If you think your application does not need as many resources as it did in the past, you can scale your resources down in the same way.
Pay-as-you-go model:
The pay-as-you-go model is probably one of the most important selling points of the cloud infrastructure. You only have to pay for the resources you use. You do not have to commit to long-term plans in which there is a chance of the extra resources going to waste and you will just have to pay for something you did not use in the first place.
Disadvantages of Cloud:
While the cloud has many major advantages, it has its own considerations as well.

Downtime:
Even though the cloud has a great mechanism to cope with downtime, it would be wrong to say that it has no downtime at all. Some technical difficulties can still occur. Bigger organizations use multiple connection channels so even if one channel goes down, the other can serve the requests of the users.
Cyber-Attacks and Security:
In a cloud-based infrastructure, your personal data is traveling through global channels alongside the data of thousands of other users. There is always an increased risk of data theft and cyber-attacks on such a network.
Latency:
Latency is one of the major disadvantages of the cloud. Since the data centers are located across the globe, and there is a lot of distance between them, it is quite difficult to get low latency values. Applications that require low latency are not suited for cloud infrastructure.
Also, read our article on the best cloud hosting startups.
How Fog Computing Works?
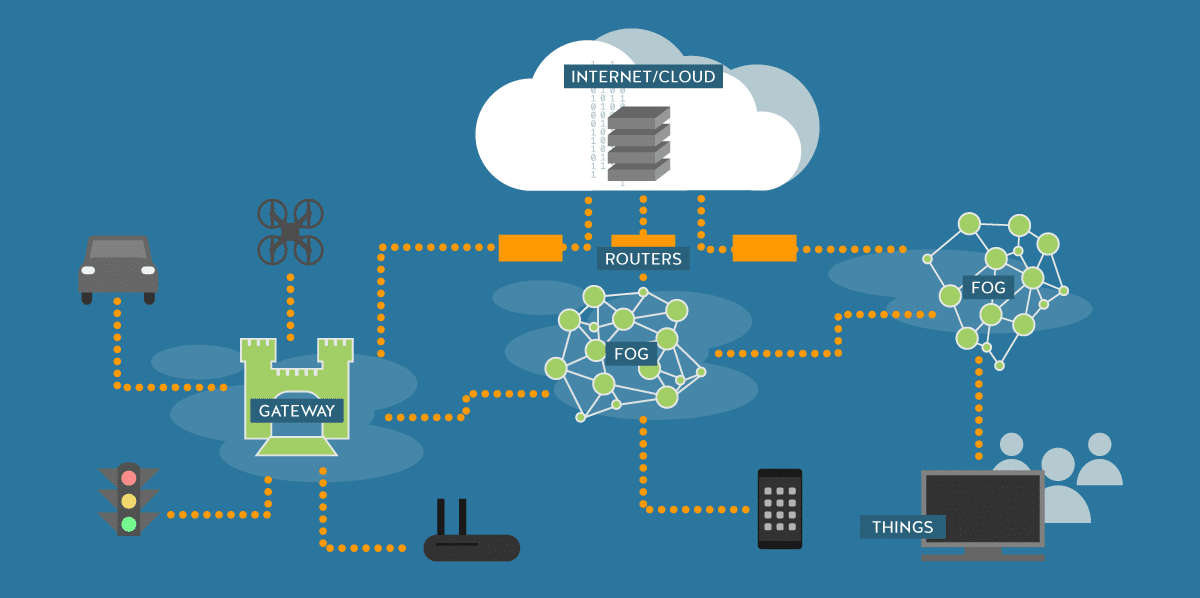
You must be wondering what is the goal of fog computing? Well, the main advantages of fog computing technology include providing the users with solutions to the problems that a simple cloud faces. So how fog computing works? Think of the whole concept as this. Fog is heavier than clouds and that is why it is closer to the earth. In this scenario, the earth is the user end devices such as computers, laptops, smartphones, etc.
Fog acts as a mediator between the clouds and the earth. So a fog computing platform is an additional layer between the cloud and the user end devices. What this does is that it decreases the distance between the servers and user devices. The fog layer consists of multiple edge nodes that are closer to user devices. Since these devices have considerable computing power, they can perform a lot of computation on their own without sending the requests back to the distant server.
Some of the fog computing examples include smart transportation networks. Each traffic device, vehicle, and even streets generate some kind of data. So to avoid accidents, the processing of a large amount of data in real-time is required. Fog computing is an efficient solution to this problem.
Advantages of Fog Computing:
Here are some of the advantages of the fog computing platform.

Low Latency:
Fog computing makes sure that you get the lowest possible latency for your application. In the cloud vs fog computing comparison, the nodes in the fog are closer to the user devices as compared to the backend cloud servers, they respond to the user requests quicker. Connecting fog and cloud computing provides an overall much faster and more secure computing architecture.
The fog layer can also contain cloudlets, which are small-scale servers located at the end of the network and their purpose is to provide support to applications that require a lot of resources and low latency.
Security:
If we do a cloud vs fog computing comparison, there is a huge difference in the level of security both of these computing infrastructures have to offer. The fog is a complex distributed system consisting of thousands of nodes and that is why it is harder for cyberattacks to work on them.
Downtime:
It is nearly impossible for a fog computing network to face downtime because of multiple interconnected channels. These multiple connections between the nodes make up for each other in case one of them fails to operate properly.
Also, read our article on google cloud alternatives.
Fog Computing vs Edge Computing:
Fog computing vs edge computing is another greatly asked for comparison by the IoT learners. The difference between them is quite simple. Think of an edge as the user end device. So the edge is basically where the data is being generated. The computing that happens at the edge of a network is called edge computing. But edge can send a massive amount of data to the cloud which can actually be irrelevant.
Fog is a layer between the edge and the cloud that decides which data is relevant and which data is irrelevant. It then separates the two and only sends the relevant data to the cloud so that the cloud is not suffocated in terms of both storage and computational power.
Conclusion:
So basically, cloud and fog computing are not two different computing architectures. Rather, fog computing is an extension of the cloud that compliments it. This concludes our article on the differences between cloud and fog computing. We hope that now you fully understand what is cloud technology and that our article on fog vs cloud computing was helpful to you.


![Cloudways vs Kinsta [Which is Better?] Cloudways Vs Kinsta](https://wphostinggeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Cloudways-VS-Kinsta-150x150.jpg)
![VPS vs Shared Hosting [Which is Better?] VPS vs Shared Hosting](https://wphostinggeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/VPS-vs-Shared-Hosting-.-150x150.png)
![Cloudways vs Siteground [Which is Faster?] Cloudways vs Siteground](https://wphostinggeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/cloudways-vs-siteground-1-150x150.jpg)
